Your Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN)Requires Professional Management
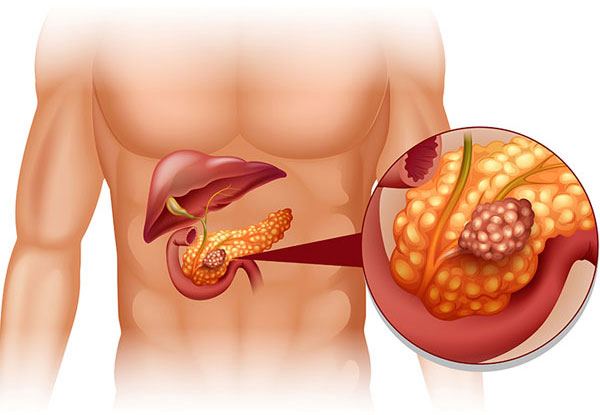
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a cystic tumor and doctors consider them precancerous. It means they aren’t cancer, but do have the potential to become cancer later in life. It is not necessary that all of these tumors develop into cancer later. It is said that 20% to 30% of cases of pancreatic cancer are caused by IPMNs.
What is an Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN)?
An intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a benign pancreatic cyst in your pancreas' ducts that has the potential to develop into a malignant, or cancerous, condition.
This type of tumor may be present for several years before any symptoms appear. IPMNs are either surgically treated.
Is Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN)malignant?
IPMNs are pre malignant. All IPMNs do not develop into cancer. However, some can develop into pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), which is the most common kind of pancreatic cancer most common kind of pancreatic cancer. But cases of pancreatic cancer are rather rare.
What results inIntraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMNs)
IPMN, develops when genes that control cell growth or prevent malignancies start to change or mutate. An IPMN is more likely to develop in those with family members who currently have or have had pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Who are affected byIntraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMNs)
Men between the ages of 50 and 70 are most likely to develop IPMNs.
What effects doesIntraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN)have on your body
IPMNs have cysts that are filled with mucin, a jelly-like material. The amount of mucin secreted increases as benign cystic tumors progress to malignancy. Pancreatic ducts can get blocked by mucin. The ducts are tiny tubes that aid in food digestion. Pancreatitis, a painful condition that may be a sign of an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, can be caused by blocked ducts.
What symptoms manifestIntraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN)
Many individuals have this condition without feeling ill or having distinct symptoms. Many people realize they have these tumors while being evaluated for other conditions. Usual signs and symptoms include:
- Intermittent stomach ache.
- Back ache.
- Unintended weight loss.
- Nausea and vomiting.
These tumors might produce symptoms that are similar to those of specific conditions, such as:
- Bile duct blockage-induced jaundice.
- Diabetes that has just started because of the effect on the pancreas.
- Pancreatitis is caused by blockage of the pancreatic bile ducts.
How do doctors diagnoseIntraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMNs)
Doctors use imaging devices, such as magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, to diagnose IPMN. It generates precise pictures of your pancreas, pancreatic duct, gallbladder, liver, and bile ducts. This test is used by doctors to check the changes in your pancreatic ducts.
What other tests are used to diagnose Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMNs)?
Endoscopic ultrasounds (EUS) may also be used by doctors to produce detailed images of your pancreas and the tumor.
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA), a type of biopsy, can be used during this procedure to obtain a sample from the tumor. The sample is then examined under a microscope for dysplasia, and genetic testing are run to estimate the risk that it will develop into cancer.
How areIntraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms (IPMNs)treated by doctors?
If an IPMN is thought to be low risk, doctors may consider closely monitoring the tumour.Many benign IPMNs don't progress to malignancy. Nonetheless, doctors may advise surgery to remove the tumor if it is located in your major pancreatic duct. Here are few instances:
- Distal pancreatectomy: Your pancreas' tail and/or body are removed by doctors, which also removes tumors discovered in the main ducts located in these regions of your pancreas.
- Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy): For malignancies located in the primary pancreatic ducts in the pancreas head, doctors may advise this surgery. Your pancreas joins to your small intestine in this region, which is its widest part. The first section of your small intestine, the duodenum, your gallbladder, the head of your pancreas, a part of your bile duct, and some adjacent lymph nodes are all removed during this surgery.
- Total pancreatectomy: Your entire pancreas, gallbladder, common bile duct, a portion of your stomach, small intestine, and, most frequently, your spleen are removed by doctors.
What can be done to lower the risk of developing anIntraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN)
This tumor develops when specific genes mutate or alter; hence, there is nothing you can do expressly to stop an IPMN from developing. To estimate your risk of IPMN and potential ways to lower it, it can be useful to follow these steps:
Those who have a family history of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma are more likely to develop IPMNs, so, you must find out about the medical history.
- Try to achieve and keep a healthy weight.
- Try to quit smoking, as it’s been connected to pancreatic cancer.
- Limit your alcohol intake or give it up altogether.
- By on healthy diet and regular exercise, to avoid getting Type 2 diabetes. Or if you have diabetes, engage with your doctor to maintain your blood sugar levels as well as possible.
A note from Dr. Neeraj in Delhi
IPMN, is a pancreatic duct tumor that has a chance of developing into pancreatic cancer. Often causing no symptoms, this tumor is frequently discovered by chance during tests done for other purposes.
When your doctor informs you that you have an IPMN, it could come as a surprise. Remember, however, that having this condition does not guarantee that you will develop cancer. Further examinations frequently reveal that the tumors are benign. If your tumor is benign, your doctor will keep a close eye out for any indications that it might become more dangerous or turn into cancer.
Whatever your circumstances, there are steps you may take to lessen your risk of developing pancreatic cancer. Talk it up with Dr. Neeraj Goel, a well-known GI surgeon in Delhi; he will be pleased to offer you his expert advice.

 info@gastrodelhi.com
info@gastrodelhi.com +91-9599294453
+91-9599294453